Buckling fundamentals
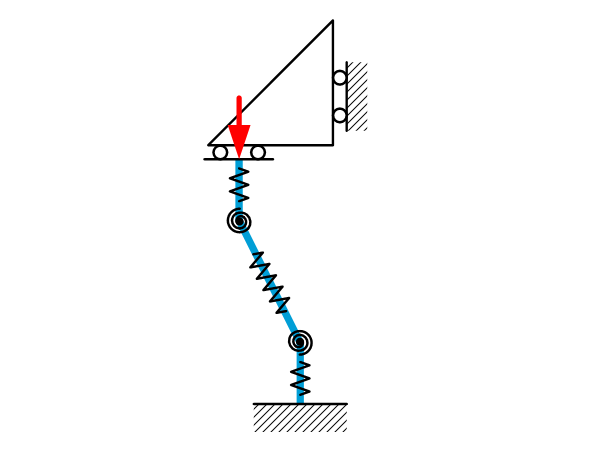
Introduction For slender structures there is a risk that buckling may occur when loaded with compression. This sheet gives an overview of how to interpret buckling and how to identify the potential risks. See Beam theory: Buckling to calculate buckling loads. What is buckling? Buckling is often seen as a failure mode of the material […]
Torsion of leaf springs: Restrained warping
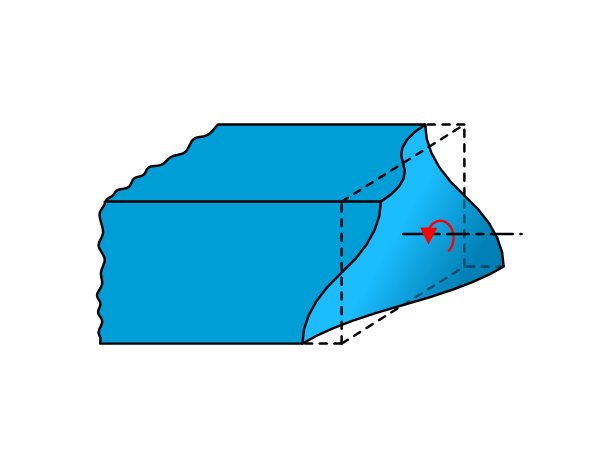
Introduction On page Beam theory: Torsion, the stiffness and shear stress due to applied torsion is presented. These equations assume the cross section of the beam is free to warp, however, this is not always true, specifically in leaf spring design. Warping due to torsion Torsion would cause the cross section of the beam to […]
Common fastener components and standards
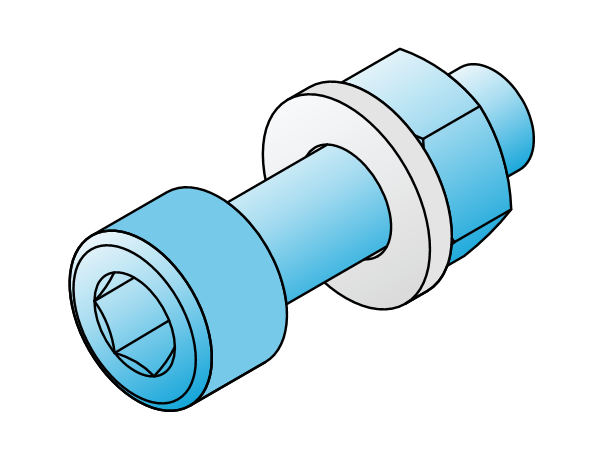
Introduction Below a table that contains commonly used fasteners sorted by fastener category. For precision engineering, commonly used fastener materials are stainless steel, brass or titanium. For applications in vacuum / cleanroom environments, fasteners that are polished, kolsterised and cleaned are recommended. Polished for reducing friction and particles, kolsterised (which is a surface hardening process) […]
Beam theory: Buckling
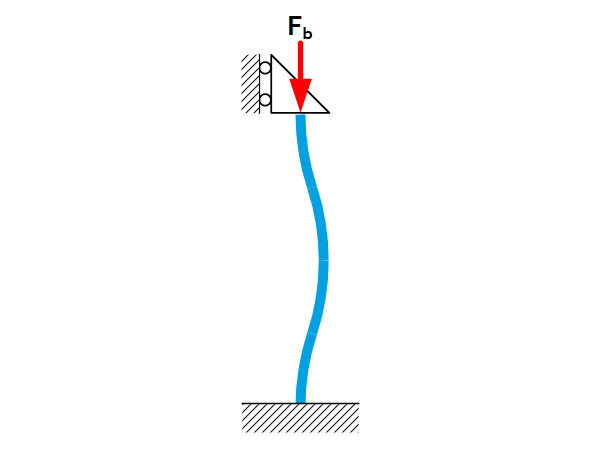
Introduction For slender structures there is a risk that buckling may occur when loaded with compression. This sheet gives the force at which buckling occurs ($F_b$) for beams with various boundary constraints. For more information on buckling see the page Buckling fundamentals. Buckling of uniform beams / leaf springs The buckling force is given by: […]
Preferred fits
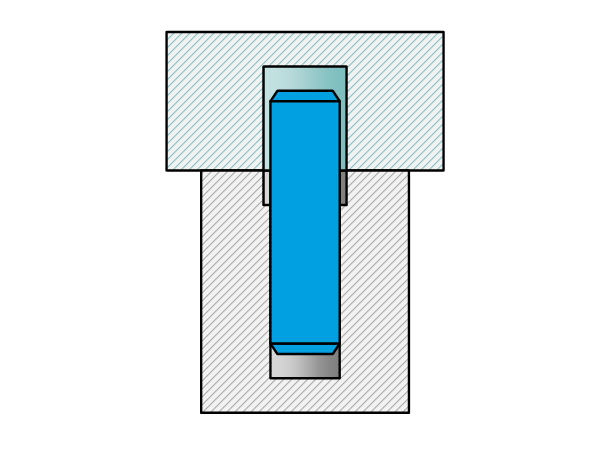
Preferred fits The table below shows the preferred fits according to ANSI B4.2-1978 with its overlap with the preferred fits of ISO 286-1 (2010) marked in green. Fits on shaft basis are preferred because of the availability of h6 dowel pins. For precision mechanisms G7/h6 is generally used as H7/h6 has a risk of getting […]
Static balancing
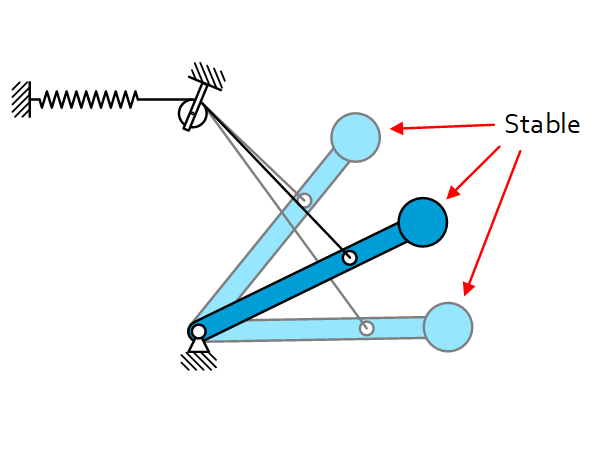
Introduction Statically balanced mechanisms are used to compensate for the gravity force of masses. Allowing these mechanisms to move from one configuration to another without the need for large actuation forces. This gravity compensation is done by using springs. Static equilibrity equation To have a static equilibrium the sum of all forces has to be […]
Beam theory: Stiffness of combined loads
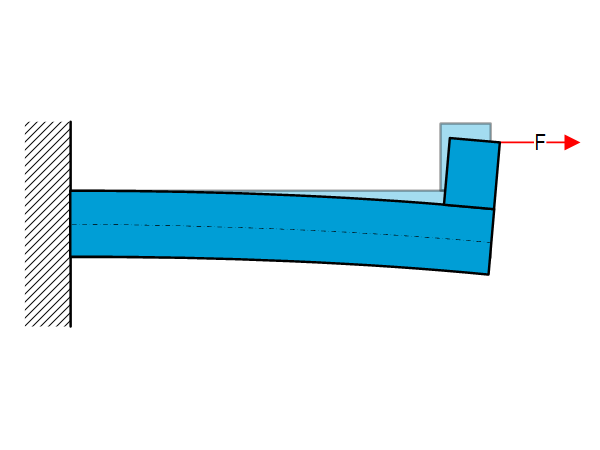
Introduction Most beam theory examples use perfect loading conditions with often a single load. But what happens when the loads are not applied at the perfect location or when a combination of loads is applied? This page aims to give some feel for the change in stiffness by giving two examples; tension/compression combined with bending […]
PiezoKnob: Actuation based on inertia and stick-slip
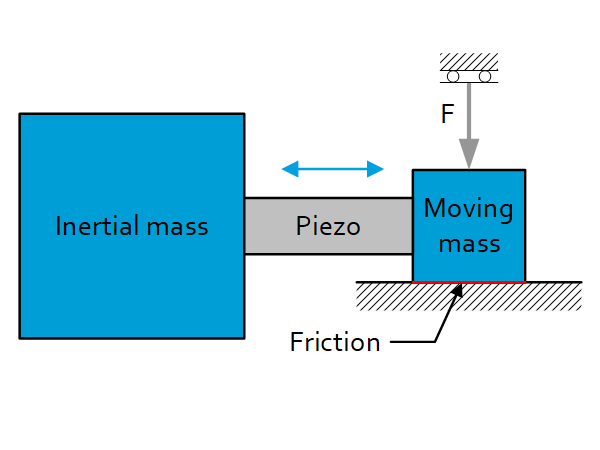
Introduction The PiezoKnob is a stepping actuator with nanometer level resolution which, when powered down, combines a high holding force with sub-nanometer stability. This is of particular interest for high precision equipment operated in vacuum and cryogenic environments where heat cannot be removed by convection and cooling power is typically limited. The inertia & stick-slip […]
Force sensor design: Example
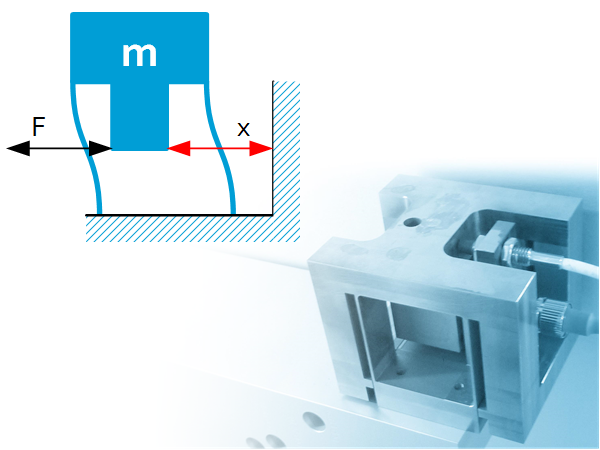
Introduction A force sensor can be obtained from a well-matched combination of a known stiffness and a displacement or strain sensor. Typically commercially available force sensors have been designed for high stiffness (> 1e6 N/m) to measure large forces (>> 10 N) which makes them unsuitable for applications requiring mN or even sub-mN resoluti0n. For […]
Cryogenic positioning stage: High resonance
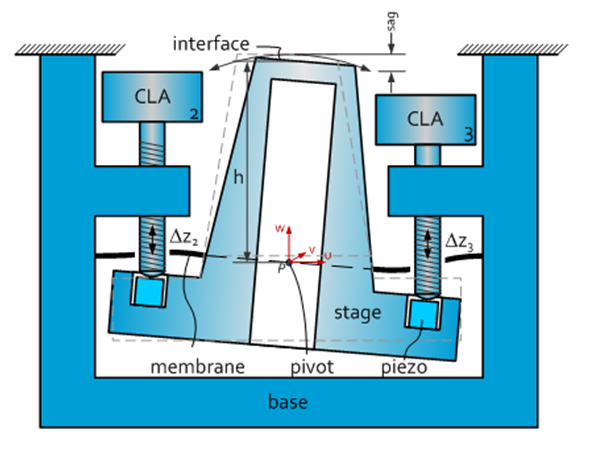
Introduction This XYZ positioning stage is specifically developed for cryogenic applications where high resonance frequencies are required. Furthermore this stage can be used in a scanning mode for small movements around a given set point. Pro’s & Con’s Operational down to 1 K High resonance frequency Sub nanometer resolution scanning mode Play/backlash free Antimagnetic materials […]
