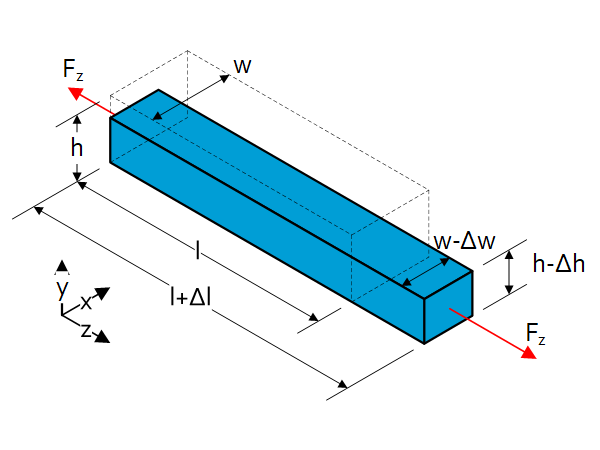
Tension/compression
Stress
$\sigma=\frac{F_z}{A}=\frac{F_z}{w\cdot h}$
Strain
$\epsilon=\frac{\Delta l}{l} $
Young’s modulus (modulus of elasticity)
The Young’s modulus is only dependent on the type of material and not on its dimensions.
$E=\frac{\sigma}{\epsilon}=\frac{F_z}{A\cdot\epsilon} $
Stiffness
In contrast with the Young’s modulus, stiffness is dependent on both the type of material and its dimensions.
$C_z=\frac{F_z}{\Delta l}=\frac{EA}{l} $
Poisson’s ratio
The Poisson’s ratio is a measure of the ratio between the transverse strain and axial strain during tension or compression.
$\nu=\frac{\frac{\Delta h}{h}}{\frac{\Delta l}{l}}=\frac{\Delta h\cdot l}{\Delta l\cdot h}\ $
Note: for metals $\nu\approx0.3$
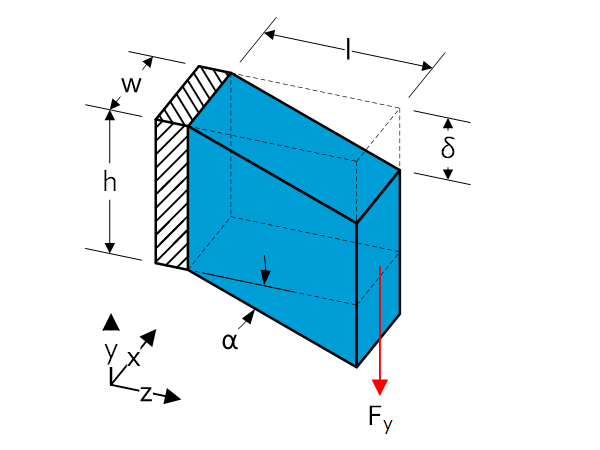
Shear
Average shear stress
$\tau=\frac{F_y}{A}=\frac{F_y}{w\cdot h}$
Shear strain
The shear strain is defined as the deformation per length. The deformation is parallel to the cross section of the beam.
$\gamma=\frac{\delta}{l}=\tan{\alpha} $
Shear modulus
$G=\frac{\tau}{\gamma\ }=\frac{F_y}{A\cdot\gamma}=\frac{E}{2\left(1+\nu\right)}$
Note: for metals $\nu\approx0.3$ thus $G\approx0.385E$
Shear stiffness
$C_y=\frac{F_y}{\delta}=\frac{G\cdot A}{l}$