Introduction
Typically struts and leaf springs demonstrate a parasitic sag-movement when moving sideways.
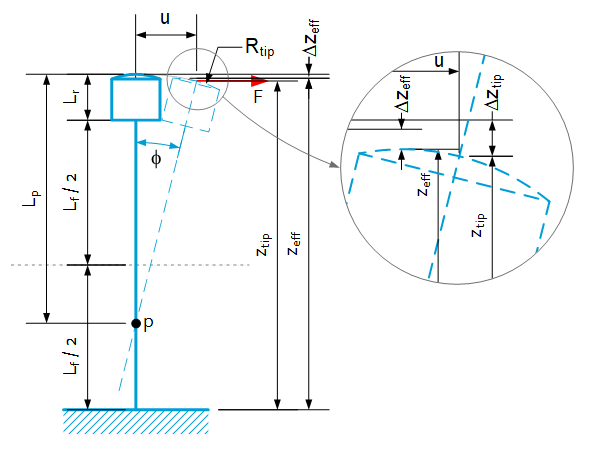
In some cases this parasitic motion is unwanted. Then a rigid tip can be implemented on the elastic element. By designing the proper tip radius, the parasitic motion can be perfectly compensated resulting in a straight-line guided motion.
Formulas
The kinematic behavior is described by the following formulas for small values of $u$, $\phi$
$z_{tip}=\left(L_r+L_f\right)-\frac{2}{15}\cdot\frac{2L_f^3+20L_r^2L_f+10L_rL_f^2+15L_r^3}{\left(2L_r+L_f\right)^2}\cdot\phi^2$
$\Delta z_{tip}=-\frac{2}{15}\cdot\frac{2L_f^3+20L_r^2L_f+10L_rL_f^2+15L_r^3}{\left(2L_r+L_f\right)^2}\cdot\phi^2$
$u_{tip}=\frac{2}{3}\cdot\frac{3L_rL_f+L_f^2+3L_r^2}{2L_r+L_f}\cdot\phi$
$L_p=\frac{u_{tip}}{\tan{\phi}}\approx\frac{u_{tip}}{\phi}=\frac{2}{3}\cdot\frac{3L_rL_f+L_f^2+3L_r^2}{2L_r+L_f}$
$z_{eff}=\left(L_r+L_f\right)+\left[\frac{R_{tip}}{2}-\frac{2}{15}\cdot\frac{2L_f^3+20L_r^2L_f+10L_rL_f^2+15L_r^3}{\left(2L_r+L_f\right)^2}\right]\cdot\phi^2$
$\Delta z_{eff}=\left[\frac{R_{tip}}{2}-\frac{2}{15}\cdot\frac{2L_f^3+20L_r^2L_f+10L_rL_f^2+15L_r^3}{\left(2L_r+L_f\right)^2}\right]\cdot\phi^2$
Special case 1: $L_r=0$ (cantilevered leaf spring / strut)
$L_p=\frac{2}{3}\cdot L_f$
$\left\{ \begin{matrix} \Delta z_{tip}=-\frac{4}{15}L_f \cdot\phi ^2 \\u_{tip}=\frac {2}{3}L_f \cdot\phi\\ \end{matrix} \right\} \Delta z_{tip}=-\frac{3}{5}\frac{u_{tip}^2}{L_f}$
Special case 2: $∆z_{eff}=0$
$R_{tip}=\frac{4}{15}\cdot\frac{2L_f^3+20L_r^2L_f+10L_rL_f^2+15L_r^3}{\left(2L_r+L_f\right)^2}$